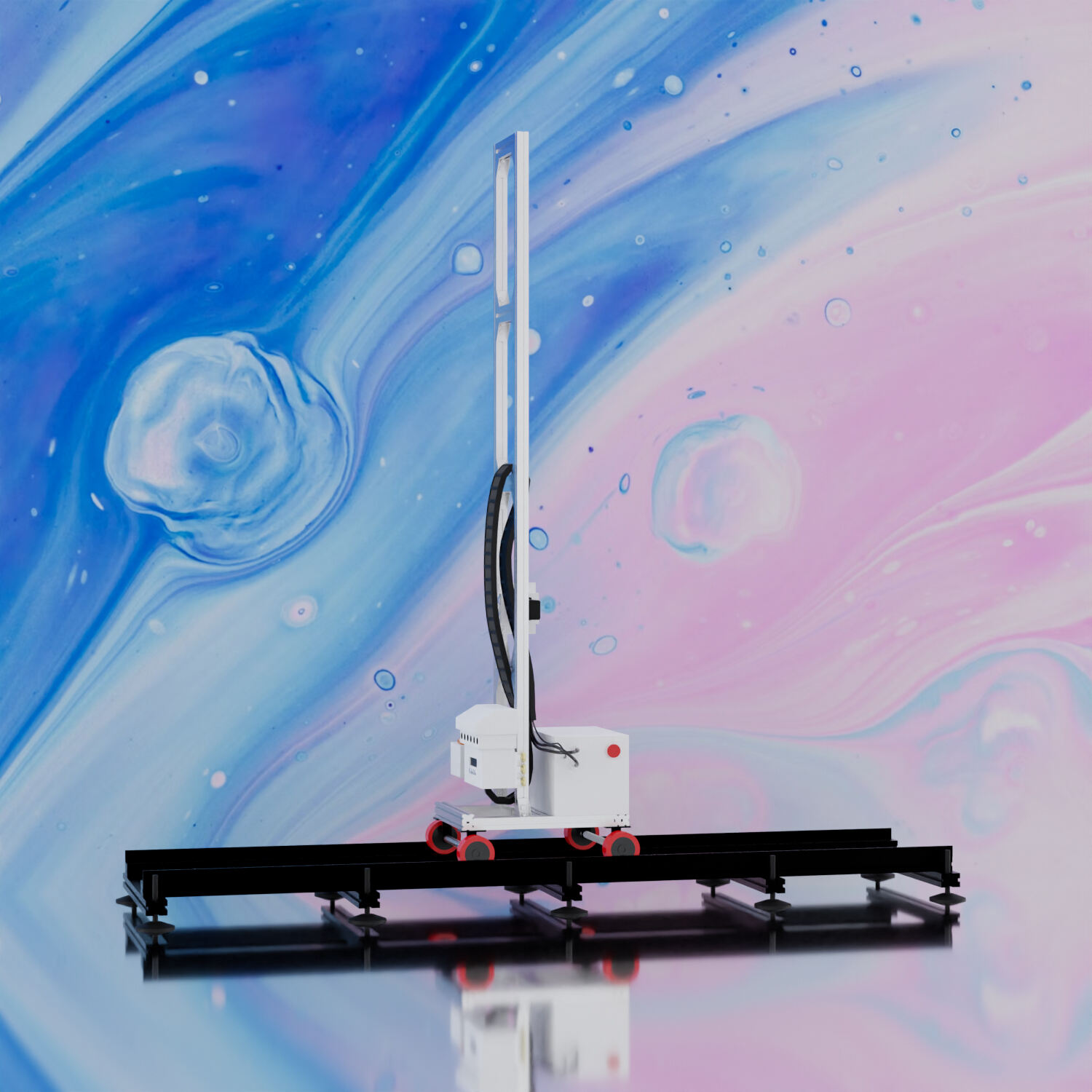
Wall mural printers are a category of automated equipment used to directly print images onto walls or vertical substrates. Their core capability comes from a stable guide rail system and a coordinated motion control system, which together determine printing accuracy, application scenarios, and efficiency. This article analyzes guide rail structure, positioning mechanisms, and motion control strategies.
1. Guide Rail Structure and Material Characteristics
The guide rail system of a wall mural printer is responsible for the stable movement of the printhead and machine body. Its common structural features include:
Guide Rail Materials
Aluminum extrusion: lightweight, portable, moderate rigidity, suitable for portable machines.
Steel materials: high rigidity and wear resistance, widely used in industrial high-precision models.
Guide Rail Connection and Extension
Modular segments are used to adjust length according to printing width.
Positioning pins, dovetail slots, or dedicated locking structures are used to ensure assembly precision.
Installation Methods and Wall Adaptation
Floor-mounted rails with shim blocks or support brackets to accommodate uneven floors.
Rail-less structures using suction or wall-mounted supports to reduce environmental dependency.
Wall adaptation includes vertical calibration, horizontal calibration, and surface flatness adjustments.
The straightness, rigidity, and assembly precision of the guide rails directly affect the stability of the printhead’s motion path.
2. Positioning Methods and Precision Assurance Mechanisms
The positioning system ensures that the printhead places ink accurately at specified coordinates on the wall. It mainly includes mechanical positioning and sensor-based positioning.
Mechanical Positioning
Travel limit blocks are used for motion range protection and preventing overrun.
Assembly reference marks are used for alignment during guide rail extension.
Sensor and Feedback Positioning
Photoelectric limit sensors are used for homing and endpoint protection.
Hall effect sensors provide non-contact limit detection with longer service life.
Encoders detect actual motor movement, including:
Incremental encoders: simple structure, low cost.
Absolute encoders: retain position information when powered off, suitable for high-precision applications.
Wall Surface Irregularity Compensation
Walls are not ideal planes and may contain bumps or tilt. Therefore, some devices are equipped with:
Laser distance modules for measuring printhead-to-wall distance
Software-based Z-axis height compensation
Geometric distortion algorithms to minimize image scaling errors
By combining hardware measurement with software compensation, surface irregularities can be effectively reduced.
3. Motion Control Methods and System Composition
The motion control system manages printhead trajectory, speed coordination, and ink firing synchronization. It is a core component of wall mural printers.
Drive Methods
Stepper motor drive for cost-controlled models with moderate precision requirements.
Servo motor drive for high-precision, high-speed, and closed-loop applications.
Motion Axis Structure
Common configurations include two or three axes:
X-axis for horizontal movement
Y-axis for vertical movement
Z-axis for distance adjustment (available in some models)
System Composition
A typical motion control system includes:
Motion controller or embedded control board
Motor drivers (stepper or servo)
Motor execution components
Limit switches and encoders for feedback
Printhead control unit for ink firing management
Trajectory Planning and Synchronization
The control system performs motion path planning and ink firing synchronization to ensure speed and ink frequency match, thereby avoiding missing lines, ghosting, or banding.
Trajectory planning commonly includes raster scanning for image printing and vector paths for lines and text.
4. Factors Affecting Motion and Positioning Performance
The overall performance of a wall mural printer is affected by multiple factors, including:
Guide rail straightness and rigidity
Motor drive precision and load capacity
Encoder resolution and feedback quality
Control system acceleration and deceleration algorithms
Wall measurement and image compensation capability
Mechanical backlash and assembly tolerances
These factors influence printing errors, repeatability, running stability, and final image quality.
Wall mural printers’ guide rail positioning and motion control methods determine precision, stability, and adaptability during actual operation. Their technical characteristics can be summarized as follows:
Guide rail structure affects running stability and application environment.
Positioning systems ensure printhead coordinate accuracy and motion boundaries.
Motion control systems handle trajectory planning and ink synchronization.
Software compensation and feedback loops improve overall print quality.
Future development trends may focus on rail-less visual positioning, high-degree-of-freedom path control, AI-based color management, and automatic wall calibration to enhance intelligence and adaptability.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 GA
GA
 BE
BE
 AZ
AZ
 KA
KA
 LA
LA
 UZ
UZ